With technological breakthroughs and industry-wide collaboration, 2025 is widely seen as the “Year of Robotics.” The entire robotics industry is experiencing explosive growth, with diverse application scenarios driving differentiated technological paths and demands for both software and hardware. Consequently, requirements and implementation methods for real-time motion control vary. Leveraging a deep understanding of the robotics sector, APQ has developed targeted real-time control optimization solutions.
01
Diverging Robotic Technology Routes & Processing Platform Selection
Bipedal humanoid robots feature a human-like design that excels in adaptability to complex terrain and whole-body coordinated operations. These robots typically require 38 to 70 axes of motion control, which means extremely high real-time requirements and control cycles up to 1000Hz. APQ uses high-performance X86 processors with software tuning to meet these real-time demands.
By contrast, wheeled or base-type robots adopt a more lightweight chassis design, offering greater advantages in cost control, motion efficiency, and battery life. These typically have around 30 degrees of freedom and lower demand for real-time computing, but are more sensitive to power consumption. For this category, APQ utilizes low-power, low-cost platforms such as Intel® N97 or J6412 to build complete solutions. This balances power efficiency and cost while leveraging the rich development ecosystem of the X86 platform to meet stringent requirements for control system real-time performance, stability, integration, and compactness.

02
APQ’s EtherCAT Real-Time Control Optimization Case Study
Application Background
Wheeled/base robots are typically used in complex trajectory control, multi-axis linkage, vision-guided motion, and similar applications. Their control systems must support:
-
EtherCAT high-speed bus communication for synchronized servo control
-
Hard real-time OS for sub-millisecond response
-
Compact industrial design suitable for tight wiring or cabinet space
-
Expandable ports including multiple serial and LAN ports for diverse peripheral integration
One client, developing a multi-axis robot, required EtherCAT support and high real-time performance. However, testing with the N97 platform and servo drivers showed that the EtherCAT communication cycle could not reach below 50μs, creating a critical bottleneck for mass production.

Real-Time Optimization Approach
Using the N97 and J6412 platforms, APQ executed full system-level real-time tuning. Example process for the N97 platform:
1. OS Switch to Linux Xenomai Environment:
-
Ubuntu 20.04 + Linux Kernel 5.15
-
Real-time patch: Xenomai 3.2 (compatible with LinuxCNC)
-
Compatibility tested for client’s legacy need (Kernel 4.19 + Xenomai 3.1)
Real-Time Tuning Steps:
a) BIOS tuning
b) Real-time kernel parameter optimization (ECI)
c) Cmdline parameter tuning (ECI)
d) Deep OS-level customization
e) Latency/Jitter measurements
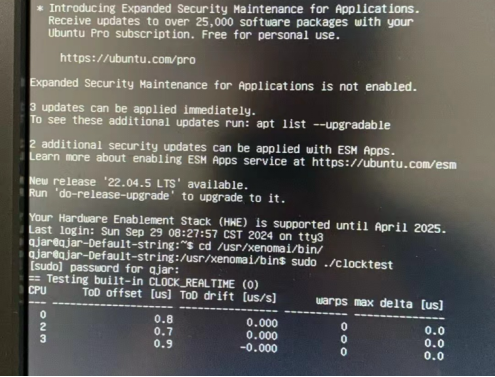
2. Standard Real-Time Testing Workflow:
-
Tools: Latency, Clocktest, LinuxCNC test modules
-
Targets:
-
Latency: Max delay < 40μs
-
Clocktest: Drift ≈ 0 (3rd column close to zero in result)
-
-
Execution: Multiple rounds of testing across hardware batches (including J6412 as comparison)
Test Result:
Under the Linux Xenomai environment, control cycle time and jitter significantly improved. The latency remained below 40μs throughout, while clocktest drift approached zero — meeting application demands.
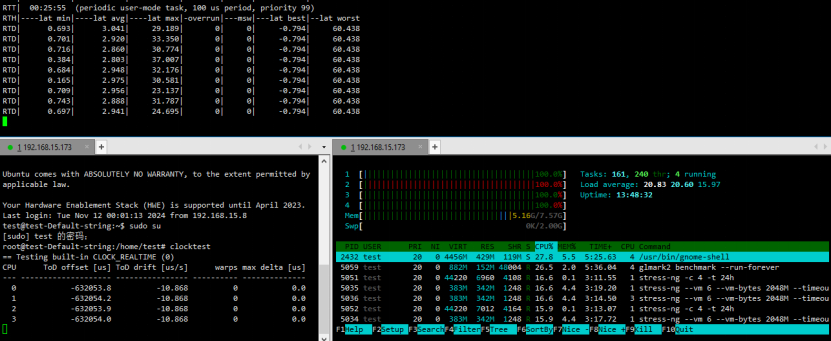
Real-World Application Outcomes
Multi-Axis Robotic Arm Control
Challenge:
8-axis synchronized welding required μs-level sync; traditional solutions caused drift and trajectory errors.
Optimization:
-
J6412 with Ubuntu 20.04 + Xenomai 3.2
-
4x Gigabit LAN direct to EtherCAT servo
-
Isolcpus dedicated real-time processing cores
Results:
-
Sync Precision: Clocktest drift ≤ 0.05μs; Max trajectory deviation < 0.1mm
-
Real-Time Assurance: 72h continuous operation, peak latency ≤ 38μs
-
Cost Reduction: 35% lower cost, 60% less power than i5 solution

Quadruped Robot Dog Motion Control
Challenge:
12-joint dynamic balancing needed μs-level feedback; legacy system latency > 100μs caused instability
Optimization:
-
N97 + Xenomai 3.2
-
PREEMPT_RT + ECI patch
-
Cmdline isolated 2 CPU cores for servo tasks
Results:
-
Low Latency: Control cycle within 500μs, latency ≤ 35μs
-
Robustness: In -20°C recovery test, jitter < ±8μs
-
Expandability: IMU sensor via M.2; 60% power savings over i3-based solution

Deployment Options
For technically capable clients focused on real-time performance, APQ recommends Linux + Xenomai deployment. For end-users preferring out-of-box convenience, APQ also offers pre-installed and optimized system images with debugging documentation — lowering deployment barriers.
As robots increasingly replace manual tasks, real-time, stable, and cost-effective control systems become critical to success. APQ is meeting this need through integrated hardware-software solutions and will continue to deepen its focus on robotic edge computing and motion control — empowering more industrial clients with stable, efficient, and easily integrated embedded platforms.
If you're interested in our company and products, feel free to contact our overseas representative, Robin.
Email: yang.chen@apuqi.com
WhatsApp: +86 18351628738
Post time: Jul-28-2025

